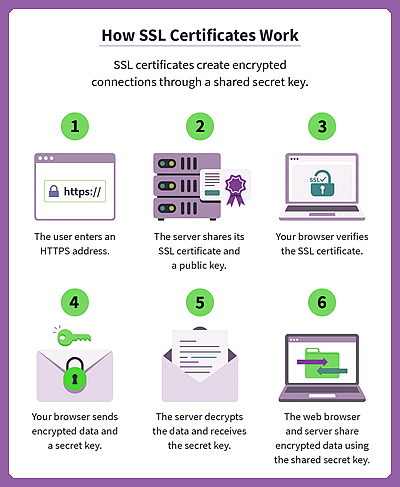
GLOSSARY: SSLAn SSL certificate is a type of digital certificate that provides authentication for a website and enables an encrypted connection. It was pioneered in 1995 by Netscape. It stands for Secure Sockets Layer. SSLs communicate to web users that a connection is safe and secure.
When a website holds an SSL certificate, a padlock icon appears on the left side of the URL address bar signifying that the connection is secure. Also the site will display an "https" address instead of an "http" address.
In order to receive an SSL certificate, the web service host must demonstrate ownership of the domain to the certificate authority at the time of certificate issuance. This authentication process is much like sealing a letter in an envelope before sending it through the mail. Today's digital citizens face many emerging threats, and making sure the websites they visit are secure is one important way they can protect their information. Secure websites help web users protect their sensitive information, like credit card or Social Security numbers - so it may be argued that sites that will not ask for such information needn't become certificated - but the 'scary message' that the site is '! Not secure' may well scare off some people from looking at your website (they may think they are more likely to be 'hacked' if they look at your site). So if you do not get an SSL certificate your Google rating will drop.
|
|

Custom Search