Cyber Security: Sharing sensitive information
 Imagine that you need to share a confidential file with a colleague in another location.
Imagine that you need to share a confidential file with a colleague in another location.
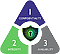
Sensitive information should only be:
 read the 'right people' (confidentiality)
read the 'right people' (confidentiality)
 changed by authorised people or processes (integrity)
changed by authorised people or processes (integrity)
 available to read and use whenever we want (availability).
available to read and use whenever we want (availability).
How should it be sent?
| E-mail |
E-mail - this is not a secure method of transmitting information – email is easily intercepted en route to its destination and there is always the risk that you send it to the wrong person! |
| Put it in the Cloud |
Use an online cloud service (Dropbox, Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive) to store the file - If you do this you have to be sure that your colleague can access the uploaded file. Also, you might also be worried about how good the security of the cloud service is against potential hackers. |
| USB pen drive |
Put the file on a USB flash memory drive and post it to your colleague - The drive could get lost in transit, stolen or intercepted by an attacker who adds malware to the drive as a way of infecting your organisation's computers. |
| Hashing |
Use encryption to lock the file against intruders. You could then email the encrypted file - safe in the knowledge that no one else could read the document. However, you would have to be sure that your colleague knows how to use encryption software so that they can decrypt the document when it arrives. |

